LED (Light Emitting Diode)
Part of Diode group
Part of Circuit Outputs group
Part of Lighting group
What it Does
LEDs emit light when current flows from the positive (+) leg to the negative (-) leg. If connected backwards, they will not light. In this way, they are like a one-way valve, allowing current to flow in one direction but not the other.
LEDs come in many different colors and brightnesses, and can be used for such things as an indicator (e.g. circuit is powered on or off), as decoration, or as a light source (e.g. LED flashlight).
What it Looks Like / Schematic Symbol
 |

Side View Top view Schematic symbol
|
How to Use
There are two ways to identify the (+) end of an LED:
1) the bulb often has a flat side that corresponds to the (-) lead (and matches the line in the schematic symbol), so the other end is the (+) lead;
2) the longer lead is the (+) lead, the shorter one is the (-) lead.
Protection resistor: LEDs require a resistor connected in series to limit the current through it (sometimes called a "current-limiting resistor"). The optimal resistor value can be calculated for a given LED, but usually a value between 100Ω and 1kΩ will work.
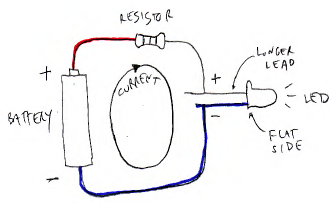 |
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM

|
The current through most common LEDs is around 20mA (0.020A).
|
The voltage needed to drive an LED depends on the color it produces.
Here is a table of common voltages.
Connection to the electromagnetic spectrum: Higher energy colors require a higher voltage to be produced.
|
 |
Tips
Soft Circuits: Bend the (+) lead into a round spiral, and bend the (-) lead into a square spiral. Or use a permanent marker to color the (+) end red and the (-) end black.

References
LED Datasheet: http://www.digitaldandt.org/db/index.php/datasheet/show/18
TEP Data Sheets: http://www.tep.org.uk/PDF/Electronics%20V1.2/data%20sheets.pdf
Duncan, Tom. Basic Skills Electronics. London: John Murray Ltd., 1988.
Duncan, Tom. Electronics for Today and Tomorrow. London: John Murray Ltd., 1985.
http://kaytdek.trevorshp.com/projects/conductive/tutorial/tutorial.html
Images
http://ledcalculator.net/
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.